Edna Burnett: How Environmental DNA Is Reshaping Conservation
So, have you ever thought about how we might truly keep track of the amazing creatures living all around us, especially those we rarely see? It's a big question, you know, when you consider how much biodiversity our planet holds. There's this really fascinating approach, a sort of silent detective, if you will, that's making a real difference in how we understand and protect wildlife. We're talking about something often referred to as Edna, a method that's got a lot of people in the conservation world pretty excited. It's a way to learn about life without even having to spot the animal itself, which is, honestly, quite remarkable.
This approach, sometimes called Edna, really does show a lot of promise, you know, for helping us watch over wildlife and support conservation efforts. It's a bit like having a new set of eyes, almost, for understanding what's out there in nature. But, you know, there's still quite a bit of work to do, too. It's not a complete solution just yet, but the progress so far is very encouraging for everyone involved. We're talking about a tool that could change how we approach environmental protection, in a way, which is a pretty big deal.
Think about it: the planet faces big challenges, like the loss of so many different kinds of plants and animals. The ocean, for instance, is absolutely vital for life on Earth, but it's under a lot of pressure, especially from changes in the climate. So, finding new ways to help is, you know, really important. This is where the ideas around Edna, or environmental DNA, truly come into play, offering a fresh perspective on how we can gather information and act to protect these precious natural spaces and the life within them.
Table of Contents
- What is Edna Burnett (Environmental DNA)?
- Why Edna Burnett Matters for Conservation
- How Edna Burnett is Used in Practice
- The Future of Edna Burnett and Ocean Insights
- Broader Sustainable Solutions
- Frequently Asked Questions About Edna Burnett
- Moving Forward with Edna Burnett
What is Edna Burnett (Environmental DNA)?
So, let's talk about what Edna, or environmental DNA, actually means. It's basically the genetic stuff that living things shed into their surroundings. Think of it like a tiny, invisible fingerprint left behind. This could be, you know, from skin cells, scales, hair, or even waste. It's pretty much everywhere an organism has been, which is quite amazing when you think about it. This material just floats around in the environment, waiting to be found. It allows us to detect and figure out what species are present without ever needing to actually see or catch the animal itself. That, honestly, makes a huge difference for researchers.
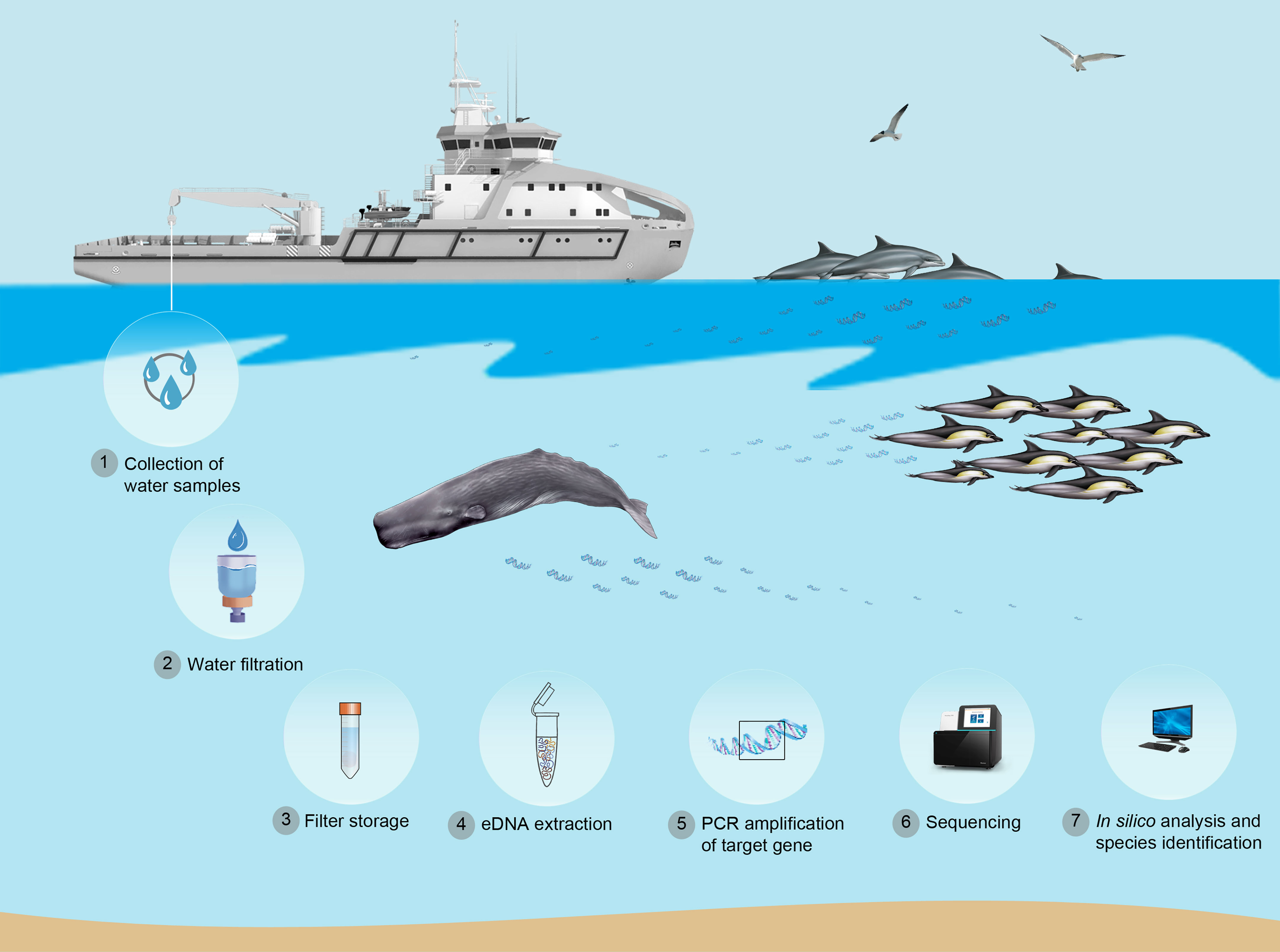
The whole idea behind Edna sampling involves gathering and then looking closely at these tiny bits of DNA. These traces are present in environmental samples, you know, like water from a river or soil from a forest floor. You collect these samples, and then you analyze them to find the DNA. This analysis helps us to detect if certain species are there, even if they're very shy or hard to spot. It's a bit like searching for clues at a crime scene, but for wildlife, in a way. This method offers a quiet, less intrusive way to understand what animals are living in a particular area, which is really helpful for conservationists.
For instance, members of a field team, like those from Pond Inlet and Salluit back in 2019, actually filtered Edna from water samples. They collected these samples from places like Milne Inlet, which is, you know, a pretty remote spot. Christopher McKindsey, who is an author, actually provided some of these insights. This kind of work shows that efforts are definitely underway to make this sampling a standard practice. It's a hands-on process, yet it relies on very small, almost invisible, pieces of information to tell a much bigger story about an ecosystem. It’s pretty clever, honestly, how it all works.
Why Edna Burnett Matters for Conservation
The loss of biodiversity, you know, is one of the biggest challenges we face right now. It means that many different kinds of life are disappearing at a rapid pace, which is, honestly, quite worrying. This is where something like Edna really steps up. It offers a fresh and very effective way to keep tabs on what's happening with species populations. If we can detect species that are rare or hard to find, we can then take steps to protect them before it's too late. It's almost like an early warning system for nature, in a way, which is pretty valuable for everyone.
Think about the ocean, for example. It's absolutely critical to the survival of life on Earth, but it's under a lot of pressure from things like the climate crisis. So, protecting it is a huge task. Edna offers a unique perspective here. By collecting water samples, scientists can find out which marine species are present, even those that live deep down or are very spread out. This information helps us understand the health of ocean ecosystems and where conservation efforts might be most needed. It’s a bit like taking the pulse of the ocean, which is, honestly, a very important thing to do right now.
This approach also plays a part in the bigger picture of economic value. The ocean, for instance, accounts for a massive amount of economic value generation, something like $44 trillion. So, when we protect these natural systems using tools like Edna, we're not just helping wildlife; we're also supporting the very foundations of human well-being and prosperity. It’s all connected, you see. A healthy environment, helped by smart monitoring like Edna, means a more stable future for everyone, which is, like, a pretty good thing to aim for.
How Edna Burnett is Used in Practice
So, how do scientists actually use Edna out in the real world? Well, it usually starts with collecting samples from the environment. This might involve, you know, taking bottles of water from a lake or ocean, or gathering scoops of soil from a forest floor. The key is that these samples contain those tiny bits of genetic material that organisms have left behind. It’s a pretty straightforward collection process, but the magic happens next, in the lab. The goal is to get a snapshot of the biological diversity in that specific area, which is, honestly, quite powerful.
Once the samples are collected, they go through a filtering process. For example, the field team members mentioned earlier, from Pond Inlet and Salluit, they literally filtered the Edna from their water samples. This step helps to separate the genetic material from other stuff in the water. After filtering, the DNA is extracted and then analyzed using special laboratory techniques. These techniques can identify the specific DNA sequences, which then tells scientists which species were present in that environment. It’s a bit like sifting through sand to find tiny gold flakes, which is, you know, pretty precise work.
Interestingly, robots are actually helping to protect the ocean, and they can play a role with Edna too. While the text doesn't explicitly say robots collect Edna, it does mention their role in ocean protection. Robots can gather samples from hard-to-reach places or cover vast areas more efficiently than humans. This kind of technology can certainly make Edna sampling more widespread and effective, particularly in challenging marine environments. It’s almost like having tireless assistants working for conservation, which is, you know, a very good thing for everyone involved in this field.
The Future of Edna Burnett and Ocean Insights
The potential for Edna, especially in our oceans, is really quite vast. Imagine optimizing whale safety, for instance. By detecting whale DNA in water samples, we could learn about their migration routes or where they spend time, without disturbing them. This kind of information could help ships avoid areas where whales are present, reducing the risk of collisions. It's a way to give these magnificent creatures a bit more space and protection, which is, honestly, a very compassionate application of this science. The possibilities for better coexistence are, you know, quite exciting.
Ocean data innovators are constantly uncovering new insights, and Edna fits right into this. Think about mapping the entire sea floor. While Edna doesn't directly map the sea floor itself, the data it provides about species distribution can be combined with physical mapping data. This creates a much richer picture of marine ecosystems. It’s about bringing together different pieces of information to see the whole puzzle more clearly. This holistic view helps to drive ocean research forward, leading to a deeper understanding of our planet’s largest habitat. It's a pretty collaborative effort, in a way.
The insights gained from Edna are helping to shape how we manage and protect our marine environments. By knowing exactly what species are present and where, conservationists can make more informed decisions about protected areas, fishing quotas, and pollution control. It’s a shift towards more precise, data-driven conservation. This kind of detailed information is incredibly valuable for policymakers and scientists alike, offering a clearer path to effective ocean stewardship. It’s almost like having a detailed health report for the ocean, which is, you know, something we really need right now.
Broader Sustainable Solutions
While Edna focuses on wildlife monitoring, it's part of a much bigger conversation about how we live on Earth. For example, the "Build Better Now" initiative at COP26 featured solutions to build more sustainably. This includes everything from one of the world’s tallest timber buildings in Sweden to a school made from bamboo in Indonesia. These examples show that we are finding new ways to create things that are less harmful to the planet. It’s about rethinking our impact, which is, honestly, a very important step for everyone.
These sustainable building practices, while different from Edna, share a common goal: protecting our natural resources and reducing our footprint. Just as Edna helps us understand and protect existing biodiversity, sustainable building aims to reduce the negative impact of human development on that very biodiversity. It’s a parallel effort, you see. Both approaches are about finding smarter, more responsible ways to interact with our environment. This kind of thinking is, you know, pretty essential for a healthy future.
It's about creating a world where economic value generation, like the $44 trillion linked to the ocean, can continue without harming the planet. This requires innovative solutions across many sectors, not just in conservation science. The drive for sustainability is a collective effort, with tools like Edna providing vital data and initiatives like "Build Better Now" showing how we can live and work more harmoniously with nature. It’s a complex challenge, but with tools and ideas like these, there's, you know, a lot of hope for progress.
Frequently Asked Questions About Edna Burnett
What is environmental DNA and how does it work?
Environmental DNA, often called Edna, is genetic material that organisms shed into their surroundings. This includes things like skin cells, waste, or hair. Scientists collect samples of water or soil, then filter and analyze these samples to find the DNA. By identifying the DNA, they can tell which species are present in that area, even if they don't see the actual animal. It's a bit like finding a biological footprint, which is, you know, pretty neat.
How is Edna collected from water samples?
Collecting Edna from water samples typically involves gathering water in special bottles. Then, in the field or a lab, this water is passed through a very fine filter. The filter traps the tiny bits of DNA that were floating in the water. This filtered material is then processed further in a lab to extract and analyze the DNA. It's a fairly simple collection method, but it requires careful handling to avoid contamination, which is, honestly, quite important.
What are the benefits of using Edna for conservation?
Using Edna for conservation offers many benefits. It allows for the detection of rare or elusive species without disturbing them. It can cover large areas more efficiently than traditional surveys. This method provides valuable data for monitoring biodiversity, tracking invasive species, and assessing the health of ecosystems. It's a powerful tool that helps conservationists make more informed decisions, which is, you know, very helpful for protecting our planet's wildlife.
Moving Forward with Edna Burnett
So, the potential for Edna, or environmental DNA, is truly significant for helping us keep an eye on wildlife and support conservation efforts. It's a bit like getting a whole new set of tools for understanding our natural world. From detecting rare species in the deepest oceans to monitoring biodiversity in remote forests, this approach offers a less intrusive and often more efficient way to gather vital information. It helps us understand the silent stories of our planet's living creatures, which is, honestly, quite a profound capability.
As we continue to face big challenges like biodiversity loss and the threats to our oceans, tools like Edna become even more valuable. They provide the kind of precise, real-time data that we need to make smart decisions about protection and management. It's about giving conservationists and policymakers the best possible information to work with. We can learn more about environmental DNA on our site, and also find out how it connects to broader efforts for a healthier planet. This kind of knowledge is, you know, pretty much essential for a sustainable future for everyone.
The ongoing work, from field teams collecting samples to innovators uncovering new insights, shows a clear path forward. It’s a collaborative effort that brings together science, technology, and a deep care for our planet. We can all play a part in supporting these efforts, whether by learning more about these technologies or by advocating for conservation. For more information on how cutting-edge science is aiding global conservation, you might want to check out resources from organizations like World Wildlife Fund. This kind of work is, you know, really making a difference, and it's something we should all be aware of, in a way, as we move forward together. You can also link to this page for additional resources.

17 Facts About Edna Mode (The Incredibles) - Facts.net

Edna Mode | Disney Wiki | FANDOM powered by Wikia
Frontiers | Environmental DNA (eDNA) for monitoring marine mammals